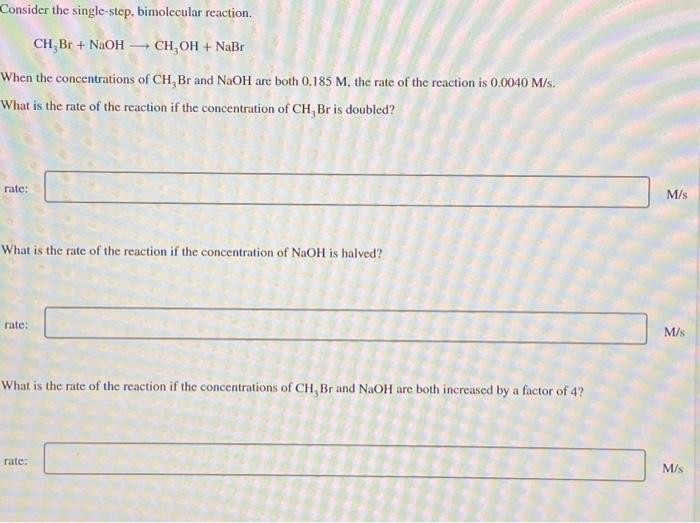
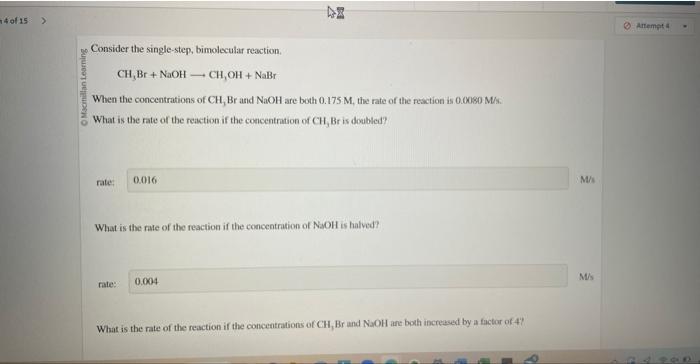
Consider the single step bimolecular reaction – Consider the single-step bimolecular reaction, a fascinating chemical phenomenon where two molecules collide and react in a single elementary step. This intricate process, characterized by its distinct mechanisms and wide-ranging applications, invites us on an enthralling journey of scientific exploration.
Delving into the heart of this reaction, we uncover the fundamental principles that govern its behavior. The collision theory provides a framework for understanding the probability of successful collisions between reactant molecules, while the rate law elucidates the relationship between the reaction rate and the concentrations of the reactants.
Define Single Step Bimolecular Reaction: Consider The Single Step Bimolecular Reaction
A single step bimolecular reaction is a chemical reaction involving the interaction of two molecules to form a single product. It is characterized by a rate law that is proportional to the product of the concentrations of the two reactants.
The reaction proceeds in a single step, without any intermediate species.
Reaction Mechanism of Single Step Bimolecular Reactions
Single step bimolecular reactions can occur through different mechanisms, including:
- Direct collision: The reactants collide with sufficient energy and orientation to form the product.
- Diffusion-controlled: The reactants diffuse together until they collide and react.
- Transition state theory: The reactants form a high-energy transition state before converting to the product.
Rate Laws and Kinetic Analysis
The rate law for a single step bimolecular reaction is given by:
Rate = k[A][B]
where:
- Rate is the rate of the reaction.
- k is the rate constant.
- [A] and [B] are the concentrations of the reactants.
The rate constant is a measure of the reaction rate and is dependent on temperature.
Factors Affecting Reaction Rates
The rate of a single step bimolecular reaction is affected by several factors, including:
- Temperature: The rate increases with increasing temperature.
- Concentration: The rate increases with increasing concentrations of the reactants.
- Solvent effects: The rate can be influenced by the polarity and viscosity of the solvent.
Applications of Single Step Bimolecular Reactions, Consider the single step bimolecular reaction
Single step bimolecular reactions have numerous applications in various fields, such as:
- Chemical synthesis: They are used in the production of various chemicals, including pharmaceuticals and polymers.
- Catalysis: They are involved in catalytic reactions, where a catalyst facilitates the reaction without being consumed.
- Environmental chemistry: They play a role in atmospheric chemistry and the removal of pollutants from water and air.
Questions and Answers
What are the key characteristics of single-step bimolecular reactions?
Single-step bimolecular reactions are characterized by their elementary nature, involving the direct collision and reaction of two molecules in a single step.
How does the rate law of a single-step bimolecular reaction differ from that of other types of reactions?
The rate law for a single-step bimolecular reaction is second-order, indicating that the reaction rate is directly proportional to the concentrations of both reactants.
What factors can influence the rate of a single-step bimolecular reaction?
The rate of a single-step bimolecular reaction can be affected by factors such as temperature, concentration, solvent effects, and the presence of catalysts.