Introducing the Formation of Ions Worksheet Answers, an invaluable resource for students seeking to master the intricacies of ion formation. This guide delves into the fundamental concepts, methods, properties, and applications of ions, providing a comprehensive understanding of this essential chemical phenomenon.
From the role of electrons in ion formation to the diverse applications of ions in various fields, this guide offers a thorough exploration of this fascinating topic.
Ion Formation
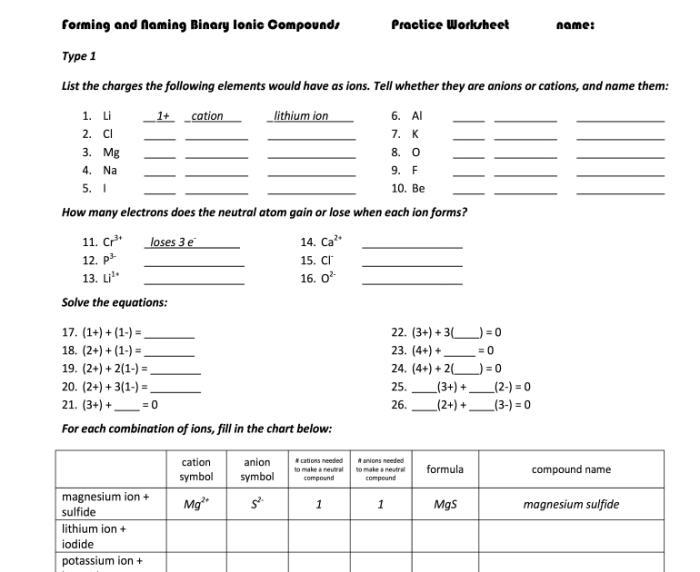
Ions are atoms or molecules that have lost or gained electrons, resulting in a net electric charge. The process of ion formation involves the transfer of electrons between atoms or molecules, leading to the creation of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions.
Electron Involvement in Ion Formation
Electrons play a crucial role in ion formation. When an atom loses one or more electrons, it becomes positively charged and forms a cation. Conversely, when an atom gains one or more electrons, it becomes negatively charged and forms an anion.
Examples of Ion Formation
Various elements undergo ion formation, including:
- Sodium (Na): When sodium loses an electron, it forms a positively charged sodium ion (Na+).
- Chlorine (Cl): When chlorine gains an electron, it forms a negatively charged chloride ion (Cl-).
- Magnesium (Mg): When magnesium loses two electrons, it forms a positively charged magnesium ion (Mg2+).
Methods of Ion Formation
Electron Loss
Ion formation through electron loss occurs when an atom or molecule loses one or more electrons. This can happen during chemical reactions, such as when a metal reacts with a non-metal.
Electron Gain
Ion formation through electron gain occurs when an atom or molecule gains one or more electrons. This can happen when a non-metal reacts with a metal.
Ion Formation in Chemical Reactions
In chemical reactions, ions can form when atoms or molecules transfer electrons to each other. This process can lead to the formation of ionic compounds, which are composed of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions.
Properties of Ions
Physical and Chemical Properties
Ions have distinct physical and chemical properties that differ from those of neutral atoms or molecules. They are typically highly reactive and can form strong bonds with oppositely charged ions.
Cations and Anions
Ions are classified into two types based on their charge: cations and anions. Cations are positively charged ions, while anions are negatively charged ions.
Common Ions and Their Properties
Some common ions and their properties include:
- Sodium ion (Na+): Monovalent cation with a +1 charge.
- Chloride ion (Cl-): Monovalent anion with a -1 charge.
- Calcium ion (Ca2+): Divalent cation with a +2 charge.
- Sulfate ion (SO42-): Divalent anion with a -2 charge.
Applications of Ion Formation, Formation of ions worksheet answers
Biological Processes
Ions play crucial roles in various biological processes, including nerve impulse transmission, muscle contraction, and maintaining fluid balance.
Industrial Applications
Ion formation has numerous industrial applications, such as in electroplating, batteries, and water purification.
Worksheet Analysis
The worksheet provides examples of ion formation from different elements. By analyzing the patterns observed in the table, we can identify:
- The relationship between the number of electrons lost or gained and the charge of the ion.
- The formation of cations from metals and anions from non-metals.
- The stability of ions with a noble gas electron configuration.
Popular Questions: Formation Of Ions Worksheet Answers
What is the significance of electrons in ion formation?
Electrons play a crucial role in ion formation. The loss or gain of electrons leads to the formation of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, respectively.
How are ions formed through chemical reactions?
In chemical reactions, ions can be formed when atoms or molecules transfer electrons to or from each other. This electron transfer results in the formation of ions with opposite charges, maintaining electrical neutrality.
What are the key differences between cations and anions?
Cations are positively charged ions formed by the loss of electrons, while anions are negatively charged ions formed by the gain of electrons. Cations are typically smaller in size than their parent atoms, while anions are larger.