Exercise 25 endocrine structure and function – Embark on an exploration of exercise 25, where we delve into the intricate structure and remarkable functions of the endocrine system. This enigmatic network of glands and hormones plays a pivotal role in regulating countless physiological processes, shaping our growth, metabolism, and overall well-being.
Our journey begins with an examination of the endocrine system’s architecture, meticulously dissecting the major glands and their hormonal secretions. We will unravel the intricate interplay between the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, orchestrating the symphony of hormone release.
1. Endocrine System Structure
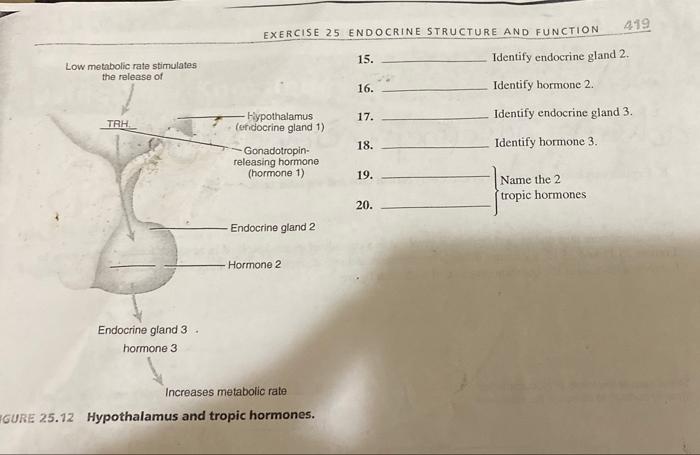
The endocrine system is a complex network of glands that secrete hormones, chemical messengers that regulate various physiological processes. It consists of:
- Endocrine glands:Glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
- Hormones:Chemical messengers that bind to specific receptors on target cells to elicit a response.
The major endocrine glands include:
| Gland | Location | Primary Hormones |
|---|---|---|
| Pituitary gland | Brain | Growth hormone, prolactin, thyroid-stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone |
| Thyroid gland | Neck | Thyroxine, triiodothyronine |
| Parathyroid glands | Neck | Parathyroid hormone |
| Adrenal glands | Above the kidneys | Cortisol, adrenaline, noradrenaline |
| Pancreas | Abdomen | Insulin, glucagon |
| Ovaries | Females | Estrogen, progesterone |
| Testes | Males | Testosterone |
The hypothalamus and pituitary gland play a crucial role in regulating hormone secretion. The hypothalamus releases hormones that stimulate or inhibit the pituitary gland, which in turn releases hormones that target other endocrine glands or directly affect target cells.
User Queries: Exercise 25 Endocrine Structure And Function
What are the major endocrine glands?
The major endocrine glands include the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas, and ovaries (in females) and testes (in males).
How do hormones regulate physiological processes?
Hormones exert their effects by binding to specific receptors on target cells, triggering a cascade of intracellular events that ultimately alter cellular function and regulate physiological processes.
What is the role of the hypothalamus in hormone regulation?
The hypothalamus serves as the master regulator of the endocrine system, releasing hormones that stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland.


