Low speed gmlan serial data – Embark on a journey into the realm of low-speed GM LAN serial data, a fascinating technology that plays a pivotal role in modern automotive systems. Discover its intricacies, applications, and the advantages it offers in a world where seamless communication is paramount.
From its humble beginnings to its advanced capabilities, this introduction provides a comprehensive overview of low-speed GM LAN serial data, setting the stage for an in-depth exploration of its inner workings.
Overview of Low-Speed GM LAN Serial Data

Low-speed GM LAN (General Motors Local Area Network) serial data is a communication protocol specifically designed for automotive applications. It is a low-cost, low-speed network that enables the exchange of data between electronic control units (ECUs) within a vehicle.
Low-speed GM LAN serial data is primarily used for non-critical applications, such as:
- Door locks
- Window controls
- Seat adjustments
- Climate control
- Infotainment systems
Benefits of Using Low-Speed GM LAN Serial Data
- Low cost and complexity
- Easy to implement and maintain
- Supports a wide range of applications
- Provides reliable data transmission
Limitations of Using Low-Speed GM LAN Serial Data, Low speed gmlan serial data
- Low data rate (typically 10-100 kbps)
- Limited range (typically a few meters)
- Not suitable for safety-critical applications
Communication Protocol
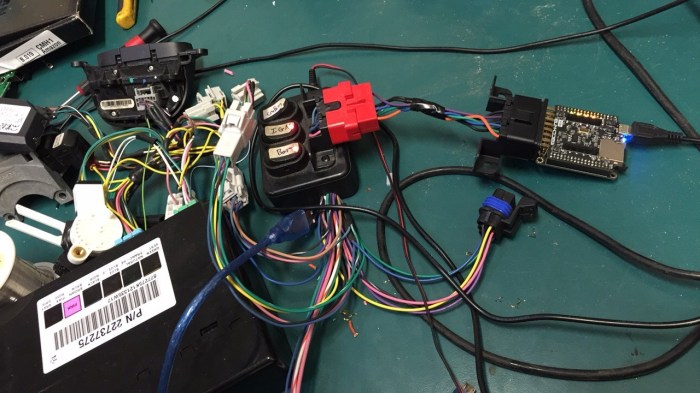
Low-speed GM LAN serial data employs a well-defined communication protocol that ensures reliable and efficient data exchange among devices on the network.
The protocol is based on a master-slave architecture, where a single master device controls the communication flow and multiple slave devices respond to requests from the master.
Message Format and Structure
Data is transmitted in the form of messages, each of which has a specific format and structure.
- Header:The header contains information such as the message type, source address, destination address, and message length.
- Payload:The payload contains the actual data being transmitted.
- CRC:The CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) is a checksum used for error detection.
Addressing Scheme
Each device on the network is assigned a unique address, which is used for addressing messages.
The addressing scheme is hierarchical, with the master device having the highest address and the slave devices having lower addresses.
Error Detection Mechanisms
The communication protocol includes several mechanisms to detect errors in data transmission.
- CRC:The CRC is a checksum that is calculated over the message data and appended to the message.
- Parity Check:The parity check is used to ensure that the number of bits in the message is even or odd, depending on the parity scheme.
Physical Layer
The physical layer defines the electrical and mechanical specifications for low-speed GM LAN serial data transmission.
It specifies the data transmission rate, signal levels, cabling requirements, and the types of connectors and termination methods used.
Data Transmission Rate
The data transmission rate for low-speed GM LAN serial data is typically 100 kbps.
Low speed gmlan serial data transmission is commonly used in automotive applications. For those interested in expanding their knowledge in real estate, consider checking out the real estate cram course ga . This comprehensive course provides valuable insights for aspiring real estate professionals.
Returning to the topic of low speed gmlan serial data, it’s worth noting that its implementation involves a combination of hardware and software components, ensuring reliable and efficient data transfer.
Signal Levels
The signal levels used for low-speed GM LAN serial data are typically 5 volts peak-to-peak.
Cabling Requirements
The cabling requirements for low-speed GM LAN serial data are typically twisted pair cables.
Connectors
The connectors used for low-speed GM LAN serial data are typically DB-9 connectors.
Termination Methods
The termination methods used for low-speed GM LAN serial data are typically 120 ohms.
Data Transmission
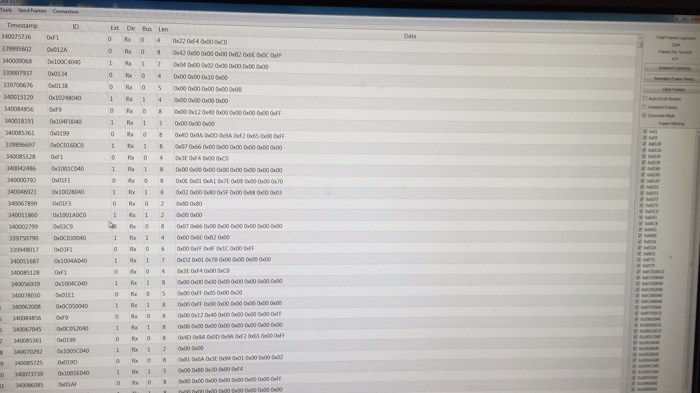
Data transmission using low-speed GM LAN serial data involves several key steps. Let’s explore the process in detail:
Framing and Synchronization
Framing ensures that data is transmitted in distinct units called frames, while synchronization ensures that the receiver and transmitter are in sync. In low-speed GM LAN, framing is achieved using start and stop bits, which define the beginning and end of each frame.
Synchronization is achieved through a synchronization field at the beginning of each frame.
Data Encoding and Decoding
Data is encoded into a form suitable for transmission over the serial line. The most common encoding scheme used in low-speed GM LAN is Manchester encoding, where each bit is represented by a transition in the signal level. Decoding involves converting the encoded signal back into its original data form.
Error Handling
In low-speed GM LAN serial data communication, error handling is crucial to ensure reliable data transmission and prevent data loss or corruption.
Several error handling mechanisms are employed to detect, correct, and recover from errors that may occur during data transmission. These mechanisms include:
Error Detection
- Parity Check:Each byte of data is accompanied by a parity bit, which indicates whether the number of 1s in the byte is even or odd. If the parity bit does not match the actual number of 1s, an error is detected.
- Checksum:A checksum is calculated by summing up all the bytes in a message and then taking the modulo of the sum by a predetermined value. The checksum is appended to the message, and the receiver recalculates the checksum and compares it with the received checksum.
If they do not match, an error is detected.
Error Correction
- Forward Error Correction (FEC):FEC codes add redundant information to the data, allowing the receiver to correct errors without retransmitting the data. The most common FEC code used in low-speed GM LAN is the Hamming code.
Error Recovery
- Retransmission:If an error is detected and cannot be corrected, the receiver requests the sender to retransmit the data. The sender will then retransmit the data using the same error handling mechanisms.
- Timeouts:If the receiver does not receive a response from the sender within a specified time period, it will assume that an error has occurred and will request the sender to retransmit the data.
Applications: Low Speed Gmlan Serial Data
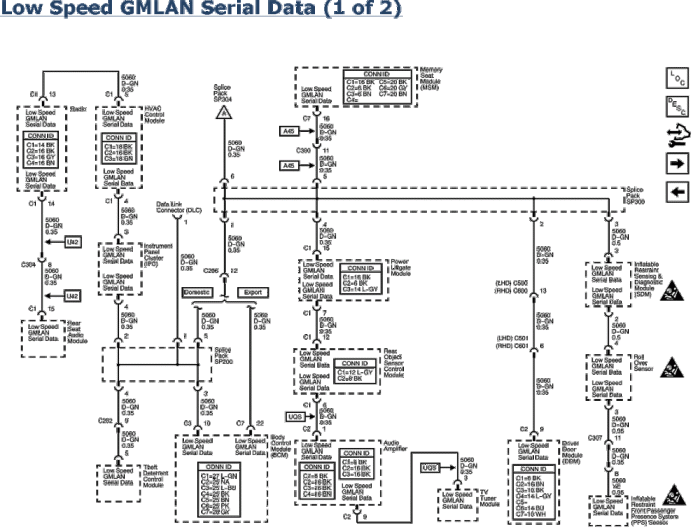
Low-speed GM LAN serial data finds applications in various automotive systems, including:
-
-*Powertrain control
Monitoring and controlling engine parameters, such as fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions.
-*Body electronics
Controlling lighting, door locks, windows, and other comfort features.
-*Safety systems
Communicating data between airbags, anti-lock brakes, and other safety devices.
- Advantages of using low-speed GM LAN serial data in these applications:
- Reliable data transmission over long distances.
- Cost-effective compared to other communication protocols.
- Easy to implement and maintain.
- Disadvantages of using low-speed GM LAN serial data:
- Limited data transmission speed compared to higher-speed protocols.
- Can be susceptible to electromagnetic interference.
- May not be suitable for applications requiring high bandwidth.
Future Trends and Advancements
The future of low-speed GM LAN serial data is expected to see advancements in:
-
-*Increased data transmission speeds
To support the growing demand for data in automotive systems.
-*Improved reliability and robustness
To enhance the stability and performance of communication networks.
-*Integration with other communication protocols
To enable seamless data exchange between different systems and devices.
-*Standardization and harmonization
To ensure interoperability and compatibility across different vehicle manufacturers.
These advancements will contribute to the continued adoption of low-speed GM LAN serial data in automotive applications, ensuring efficient and reliable communication within vehicle systems.
FAQ Guide
What is the purpose of low-speed GM LAN serial data?
Low-speed GM LAN serial data facilitates communication between electronic control units (ECUs) in automotive systems, enabling the exchange of critical information for various functions, including engine management, transmission control, and safety features.
What are the benefits of using low-speed GM LAN serial data?
Low-speed GM LAN serial data offers several advantages, including low cost, high reliability, ease of implementation, and low power consumption, making it an ideal choice for a wide range of automotive applications.
What are the limitations of low-speed GM LAN serial data?
One limitation of low-speed GM LAN serial data is its relatively low data transmission rate compared to other communication protocols. Additionally, its use is primarily limited to short-distance communication within a vehicle.